– 20 Stunning Facts About Energy Jobs In The US (ZeroHedge, Dec 22, 2014):
For all those who think the upcoming carnage to the shale industry will be “contained” we refer to the following research report from the Manhattan Institute for Policy Research:
- The United States is now the world’s largest and fastest-growing producer of hydrocarbons. It has surpassed Saudi Arabia in combined oil and natural gas liquids output and has now surpassed Russia, formerly the top producer, in natural gas. [ZH: that’s about to change]
- The increased production of domestic hydrocarbons not only employs people directly but also radically reduces the drag on growth and job formation associated with America’s trade deficit.
- As the White House Council of Economic Advisors noted this past summer: “Every barrel of oil or cubic foot of gas that we produce at home instead of importing abroad means more jobs, faster growth, and a lower trade deficit.” [the focus now is not on the oil produced at home, which is set to plunge, but the consumer “tax cut” from plunging oil prices]
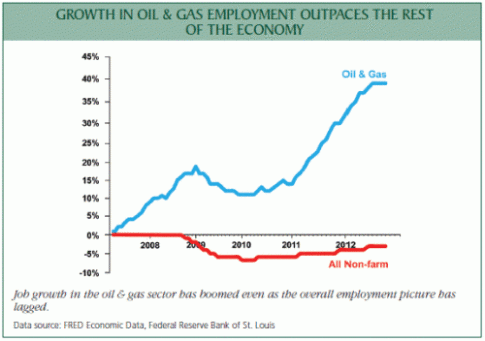
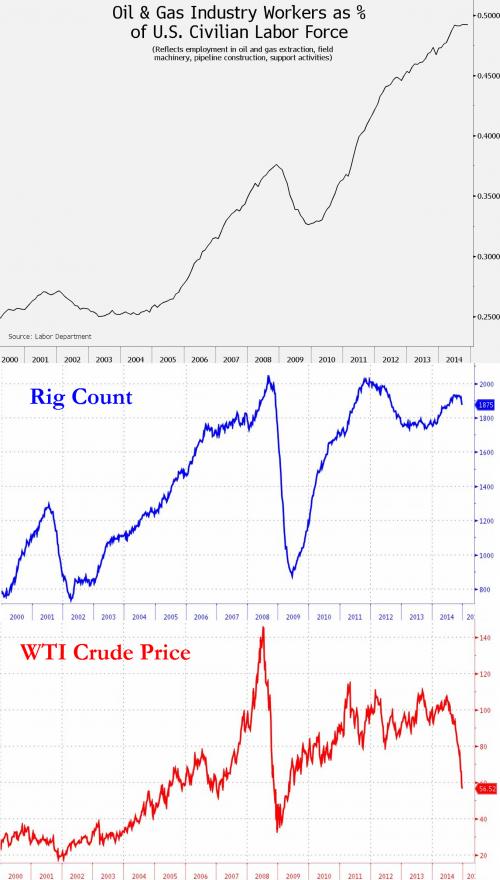
- Since 2003, more than 400,000 jobs have been created in the direct production of oil & gas and some 2 million more in indirect employment in industries such as transportation, construction, and information services associated with finding, transporting, and storing fuels from the new shale bounty.
- All told, about 10 million Americans are employed directly and indirectly in a broad range of businesses associated with hydrocarbons.
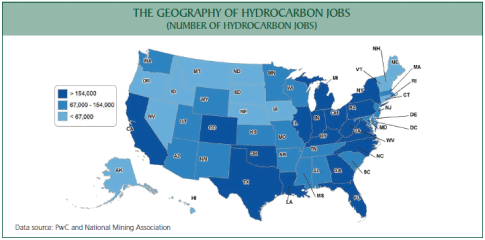
- There are 16 states with more than 150,000 people employed in hydrocarbon-related activities. Even New York, which continues to ban the production of shale oil & gas, is seeing job benefits in a range of support and service industries associated with shale development in adjacent Pennsylvania.
- Direct employment in the oil & gas industry had been declining for 30 years but has recently reversed course, with the availability of new technologies to developshale fields. Nearly 300,000 direct oil & gas jobs have been created following the 2003 nadir in that sector’s direct employment.
- The five super-major oil companies—Exxon, BP, Chevron, Shell, Conoco—that operate in the U.S. account for only 10 percent of Americans working directly in the oil & gas business.
- Meanwhile, more than 20,000 other firms are directly involved in the oil & gas industry, and they produce over 75 percent of America’s oil & gas output. The median independent oil & gas firm has fewer than 15 employees. (Note that these data exclude gasoline stations, which employ nearly 1 million people and are overwhelmingly owned by individuals or small businesses.)
- As in the oil & gas industry, most Americans are employed by firms with fewer than 500 employees. Small businesses not only employ half of all American workers but also generate nearly half the nation’s economic output. Young firms tend to be small firms; and young firms tend to emerge disproportionately in areas of rapid growth or new opportunities—such as in and around America’s shale fields.
- A broad array of small and midsize oil & gas companies are propelling record economic and jobs gains—not just in the oil fields but across the economy. The enormous expansion in employment, exports, and tax revenues from the domestic oil & gas revolution is largely attributable to a core and defining feature of America: small businesses.
- The oil & gas sector boom creates “induced” and energy-related jobs. For every direct job, there are, on average, three jobs created in industries such as housing, retail, education, health care, food services, manufacturing, and construction.
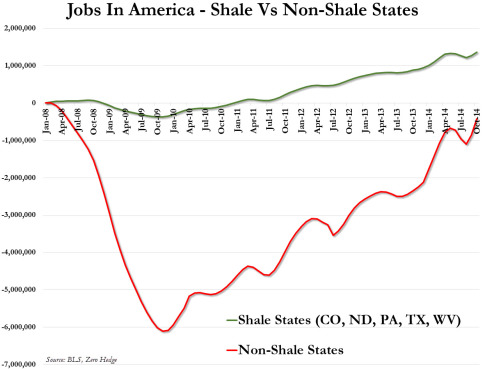
- In the 10 states at the epicenter of oil & gas growth, overall statewide employment gains have greatly outpaced the national average. There we see the ripple-out effect on overall (not just oil & gas) employment. The shale boom’s broad jobs benefits are most visible in North Dakota and Texas, of course, where overall state employment growth in all sectors has vastly outpaced U.S. job recovery. Similarly, in the other states that have experienced recent growth in hydrocarbon production—notably, Pennsylvania, Colorado, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Wyoming—statewide overall (again, not just oil & gas) employment growth has also outpaced the U.S. recovery.
- In addition to the direct and induced jobs, America is beginning to see the economic and jobs impact of a renaissance in energy-intensive parts of the manufacturing sector, from plastics and chemicals to fertilizers. Examples include an Egyptian firm planning a $1 billion fertilizer plant in Iowa and a South Korean tire company with an $800 million plan for a Tennessee plant. Germany’s BASF recently announced expansion of its American investments, including production and research. BASF calculated that its German operations’ energy bill would be $700 million a year lower if it could pay American prices for energy
- The Marcellus shale fields in Pennsylvania were responsible for enabling statewide double-digit job growth in 2010 and 2011 and now account for more than one-fifth of that state’s manufacturing jobs. For every $1 that the Marcellus industry spends in the state, $1.90 of total economic output is generated.
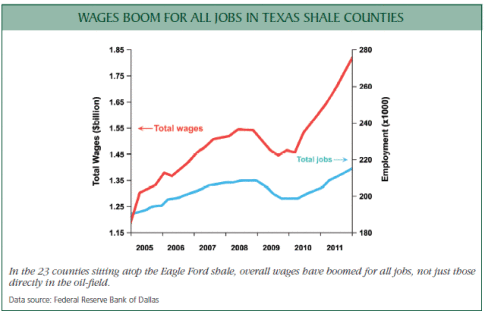
- The typical wage effect of the oil & gas revolution is most clearly visible in Texas. In the 23 counties atop the Eagle Ford shale, average wages for all citizens have grown by 14.6 percent annually since 2005, compared with the 6.8 and 6.3 percent average for Texas and the U.S., respectively, over the same period. The top five counties in the Eagle Ford shale have experienced an average 63 percent annual rate of wage growth. These are the kinds of wage effects sought in every state and by every worker.
- Given the persistent, slow job recovery from the Great Recession, there could not be a more important time in modern history to find ways to foster more small businesses of all kinds, given that they are not only the core engine for growth but also frequently grow rapidly.
Punchline #1:
- The $300–$400 billion overall annual economic gain from the oil & gas boom has been greater than the average annual GDP growth of $200–$300 billion in recent years—in other words, the economy would have continued in recession if it were not for the unplanned expansion of the oil & gas sector.
Punchline #2:
- Hydrocarbon jobs have provided a greater single boost to the U.S. economy than any other sector, without requiring any special taxpayer subsidies—instead generating tax receipts from individual incomes and business growth.
And the final punchline:
- The National Association of Manufacturers estimated that the shale revolution will lead to 1 million manufacturing jobs over the coming decade. Manufacturing jobs pay nearly 30 percent more than the industrial average and generate $1.48 of economic activity for every $1 spent, making manufacturing the highest economic multiplier of all industrial sectors.
Sorry, not anymore.
Now, thanks to John Kerry’s “secret pact“, and America’s close “ally” in the middle-east, Saudi Arabia whose “mission” it no longer to bankrupt Russia but to crush America’s shale inddstry, the only question surround the only bright spot for America’s economy over the past 6 years is how long before most of the marginal producers file Chapter 11, or 7.